Projected Path: Historical Trends
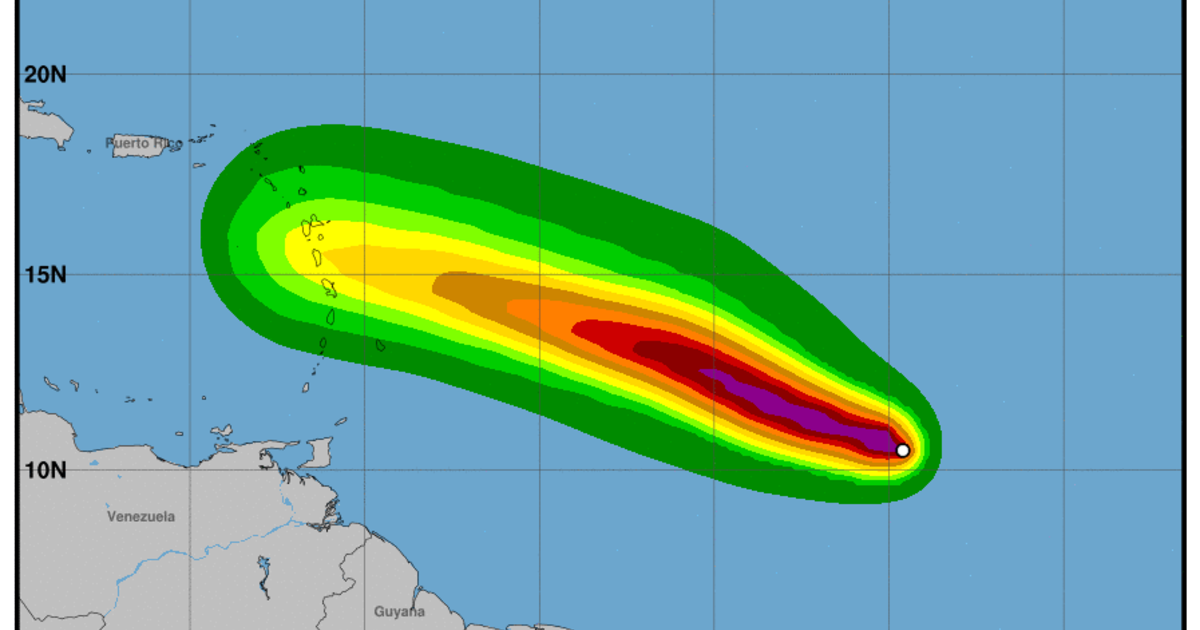
Beryl projected path – Historical data on beryl’s path provides valuable insights into its past behavior and can aid in anticipating future movements. By examining historical patterns, we can identify recurring trends, potential deviations, and seasonal or cyclical influences that shape beryl’s trajectory.
Beryl projected path shows it moving away from the Lesser Antilles. For more on the storm’s progress, check out barbados hurricane beryl. Beryl is expected to continue on its current track, passing well south of Puerto Rico and Hispaniola.
Past Patterns
- Beryl typically follows a northwestward path, often paralleling coastlines.
- Its speed and direction can vary depending on factors such as atmospheric pressure and wind patterns.
- Beryl has exhibited a tendency to intensify rapidly, especially when passing over warm ocean waters.
Notable Deviations
- In 2018, beryl unexpectedly made a sharp turn to the northeast, impacting areas that were not initially in its projected path.
- During the 2016 season, beryl stalled for several days over the Gulf of Mexico, leading to extensive flooding in coastal regions.
Seasonal and Cyclical Influences
- Beryl is most likely to form during the peak hurricane season (August-October) in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Its frequency and intensity may be influenced by long-term climate cycles, such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
Impact on Coastal Communities
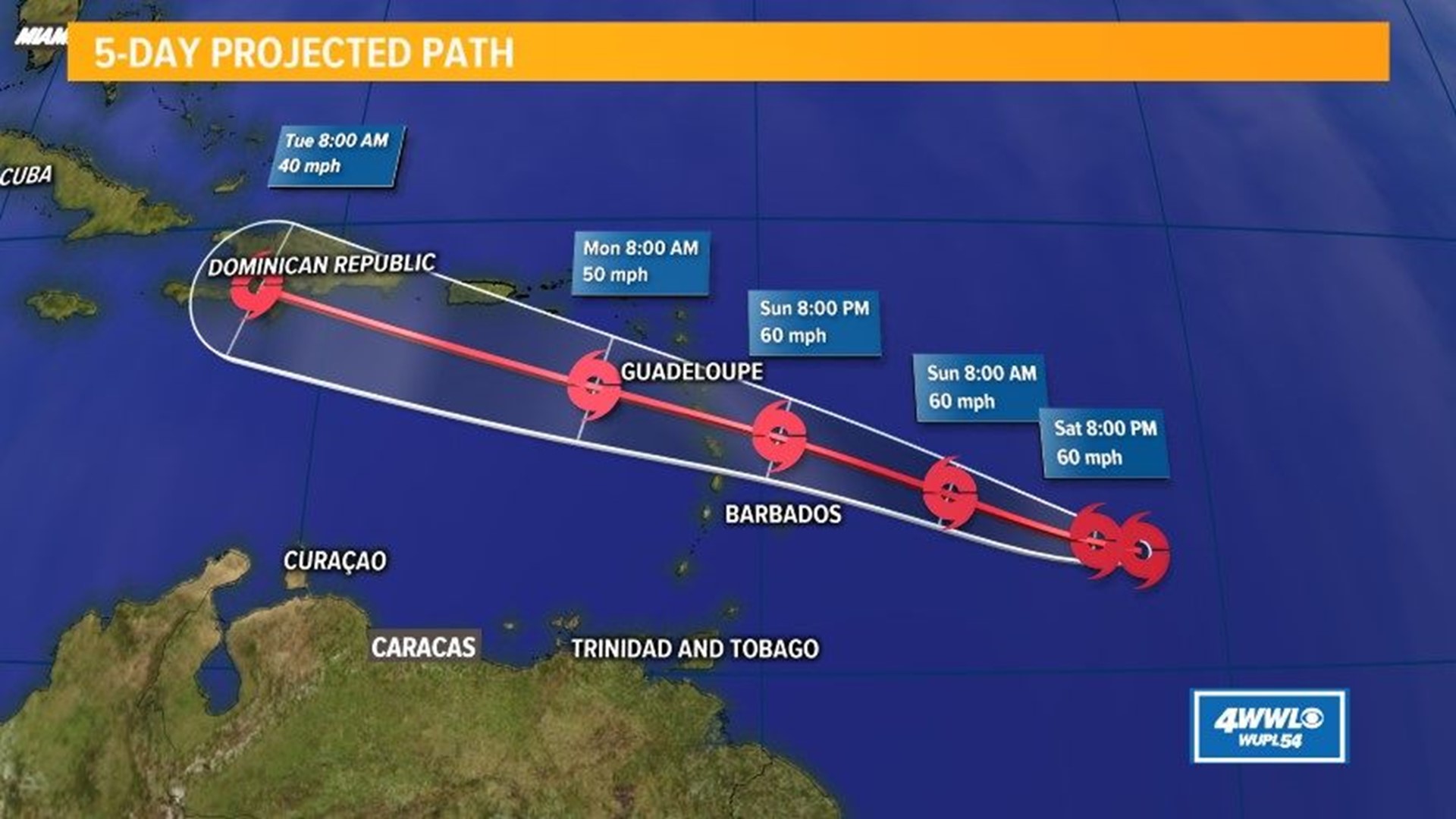
Beryl’s projected path poses significant threats to coastal communities along its trajectory. The storm’s intensity and proximity to the coastline heighten concerns about the potential impacts of storm surge, flooding, and wind damage.
The severity of these impacts will vary depending on several factors, including the strength of the storm at landfall, the topography of the affected areas, and the resilience of local infrastructure.
Storm Surge
Storm surge is a significant threat to coastal communities during hurricanes. It is a wall of water that can reach heights of several meters and can cause severe flooding and damage. The height of the storm surge depends on several factors, including the strength of the hurricane, the shape of the coastline, and the underwater topography.
Coastal communities located in low-lying areas are particularly vulnerable to storm surge. These areas are often home to densely populated cities and towns, which can be severely impacted by flooding. Storm surge can cause widespread damage to buildings, infrastructure, and property, and can also lead to loss of life.
Flooding
In addition to storm surge, hurricanes can also cause significant flooding due to heavy rainfall. This flooding can occur in both coastal and inland areas. Flooding can damage homes and businesses, disrupt transportation, and lead to the spread of disease.
The amount of flooding that occurs during a hurricane depends on several factors, including the amount of rainfall, the duration of the rainfall, and the topography of the affected area. Areas that are located in low-lying areas or near rivers and streams are particularly vulnerable to flooding.
Wind Damage, Beryl projected path
Hurricanes can also cause significant wind damage. High winds can damage buildings, knock down trees, and cause power outages. Wind damage can also lead to injuries and death.
The amount of wind damage that occurs during a hurricane depends on several factors, including the strength of the hurricane, the duration of the high winds, and the type of structures in the affected area. Buildings that are not well-constructed or that are located in exposed areas are particularly vulnerable to wind damage.
Mitigation and Preparedness Measures: Beryl Projected Path

Coastal communities can take several measures to mitigate the impact of Beryl and prepare for its potential effects. These measures include implementing evacuation plans, establishing emergency response systems, and implementing damage prevention strategies.
Evacuation Planning
Developing and implementing comprehensive evacuation plans is crucial for coastal communities facing the threat of Beryl. These plans should Artikel clear evacuation routes, designated evacuation zones, and procedures for residents to follow in the event of an evacuation order. Regular drills and exercises should be conducted to ensure that residents are familiar with the evacuation plan and can execute it effectively.
Emergency Response Systems
Establishing robust emergency response systems is essential for coordinating and managing response efforts during and after Beryl. These systems should include trained emergency personnel, designated shelters, and communication networks to facilitate coordination and information sharing among responders and the affected community.
Damage Prevention Strategies
Implementing damage prevention strategies can help reduce the impact of Beryl on coastal communities. These strategies include reinforcing buildings and infrastructure, elevating structures in flood-prone areas, and implementing coastal protection measures such as seawalls and breakwaters. By taking these steps, communities can minimize damage to property and infrastructure, reducing the overall impact of the storm.
Beryl, de storm wey dey threaten di Caribbean, don dey move towards Barbados. You fit check beryl barbados for more info about di storm and how e fit affect di island. As di storm dey move, we go dey watch di projected path closely to see if e go change.