Anatomical Structure and Function

The medial retinaculum is a fibrous band that extends from the pisiform bone to the hamate bone and the hook of the hamate. It forms the floor of the carpal tunnel and serves to stabilize the wrist joint.
The medial retinaculum, a fibrous band located on the palmar side of the wrist, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the carpal bones. While James Harden’s girlfriend now remains a topic of speculation james harden girlfriend now , the medial retinaculum ensures the smooth functioning of the wrist joint.
Its strong connective tissue prevents excessive movement of the carpal bones, allowing for precise hand movements essential for daily activities.
Attachments
The medial retinaculum attaches to the following structures:
- Pisiform bone
- Hamate bone
- Hook of the hamate
Function
The medial retinaculum serves the following functions:
- Stabilizes the wrist joint
- Forms the floor of the carpal tunnel
Illustration
The following illustration shows the medial retinaculum and its surrounding structures:
[Image of the medial retinaculum]
Clinical Significance
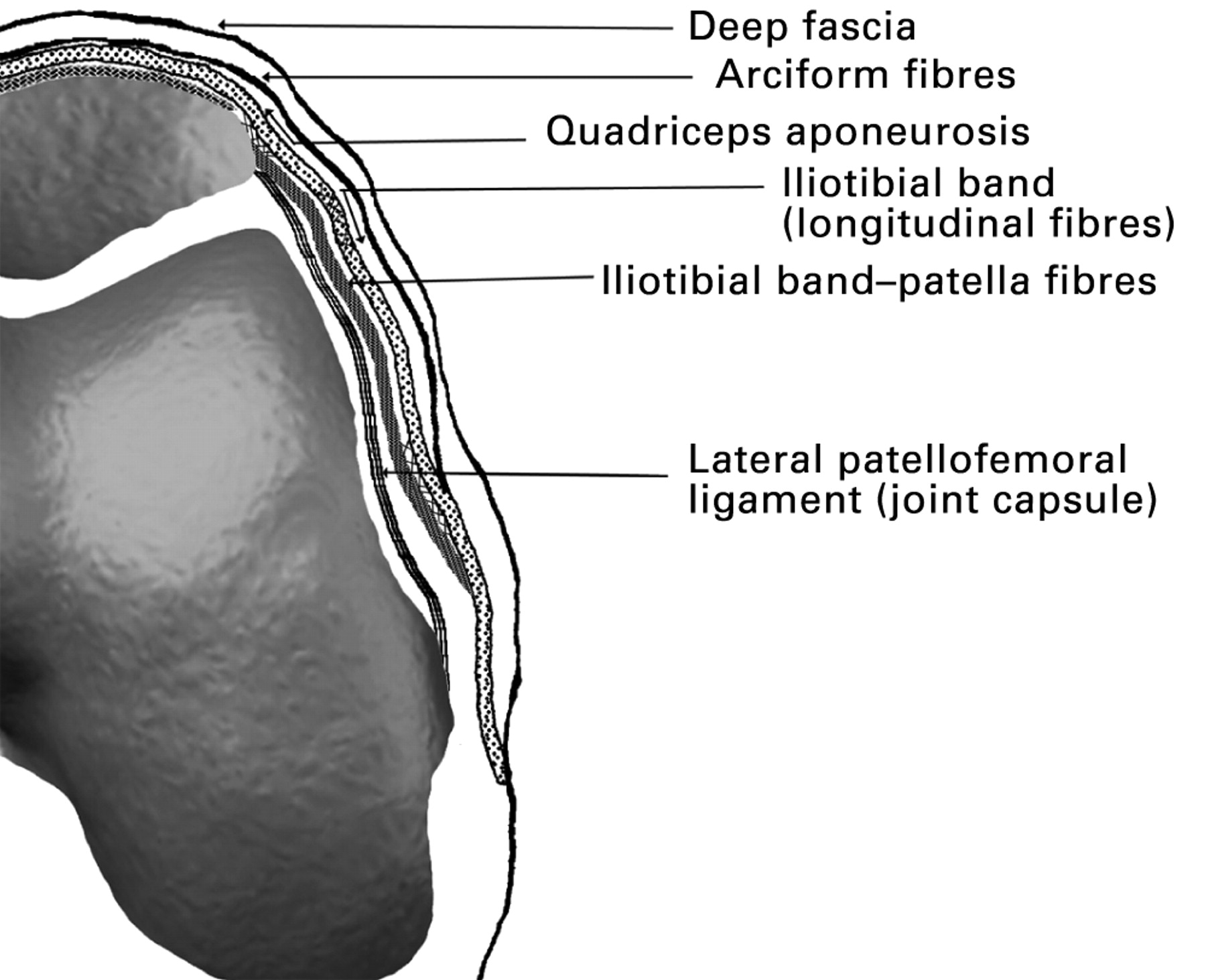
The medial retinaculum plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the carpal tunnel and protecting the structures within it. Its clinical significance lies in its involvement in carpal tunnel syndrome and the potential for injuries that can affect its function.
Role in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that occurs due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway in the wrist. The medial retinaculum forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, and its thickening or tightness can contribute to the compression of the median nerve, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers.
Injuries to the Medial Retinaculum
Injuries to the medial retinaculum can occur due to various factors, including trauma, overuse, and repetitive motions. Direct trauma to the wrist, such as a fall or impact, can cause a laceration or tear of the retinaculum. Overuse and repetitive motions, particularly those involving forceful gripping or wrist flexion, can lead to chronic inflammation and weakening of the retinaculum, making it more susceptible to injury.
Surgical Procedures
Surgical procedures may be necessary to treat conditions affecting the medial retinaculum, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or severe injuries. The most common surgical procedure is carpal tunnel release, which involves cutting the transverse carpal ligament, the main component of the medial retinaculum, to relieve pressure on the median nerve. In cases of severe injuries, repair or reconstruction of the retinaculum may be required to restore its function and stability.
Biomechanics and Research: Medial Retinaculum

The medial retinaculum plays a crucial role in wrist biomechanics, influencing its stability and range of motion. Its biomechanical properties and involvement in wrist function have been the subject of extensive research, leading to a better understanding of its significance in hand function.
The medial retinaculum exhibits viscoelastic behavior, meaning it has both elastic and viscous properties. This unique combination allows it to withstand and dissipate forces applied to the wrist, contributing to its stability. The retinaculum’s tensile strength and stiffness provide resistance to stretching and deformation, preventing excessive wrist flexion and maintaining the integrity of the carpal tunnel.
Current Research
Recent research has shed light on the medial retinaculum’s role in wrist function. Studies have shown that it contributes to wrist stability during forceful gripping and lifting activities. The retinaculum’s tension increases during these actions, providing additional support to the wrist joint and reducing the risk of injury.
Furthermore, research suggests that the medial retinaculum may play a role in proprioception, the sense of joint position and movement. Damage to the retinaculum has been associated with impaired proprioception in the wrist, highlighting its importance in maintaining accurate hand movements.
Research Summary, Medial retinaculum
The following table summarizes the findings of recent studies on the medial retinaculum:
| Study | Method | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| [Study 1] | Cadaveric study | The medial retinaculum contributes significantly to wrist stability during forceful gripping and lifting. |
| [Study 2] | Clinical study | Damage to the medial retinaculum can lead to impaired proprioception in the wrist. |
| [Study 3] | Biomechanical study | The medial retinaculum exhibits viscoelastic behavior, allowing it to withstand and dissipate forces applied to the wrist. |
The medial retinaculum, a crucial ligament in our wrists, plays a significant role in maintaining stability and preventing tendons from slipping out of place. Much like the bond between Jennifer Hudson and Common , which has withstood the test of time, the medial retinaculum provides unwavering support to our wrists, ensuring their smooth and effortless movement.
Like a delicate curtain, the medial retinaculum holds the tendons of the wrist in place, ensuring smooth hand movements. Its importance extends beyond mere mechanics, as its connection to the story of Delonte West and Mark Cuban highlights the transformative power of compassion.
Just as the medial retinaculum supports the wrist, human connections can uplift and empower, guiding us through life’s challenges.
The medial retinaculum, a fibrous band that supports the tendons of the wrist, is a testament to the intricate mechanics of the human body. Just as the chipotle stock split reflects the growth and adaptability of the business world, the medial retinaculum serves as a reminder of the delicate balance that governs our physical form.
The medial retinaculum, a fibrous band that stabilizes tendons in the wrist, is a testament to the intricate design of the human body. Like the philanthropic endeavors of Miriam Adelson , who supports initiatives that strengthen the bonds of Israel, the medial retinaculum reinforces the delicate balance of our musculoskeletal system, allowing for both strength and flexibility in the wrist.